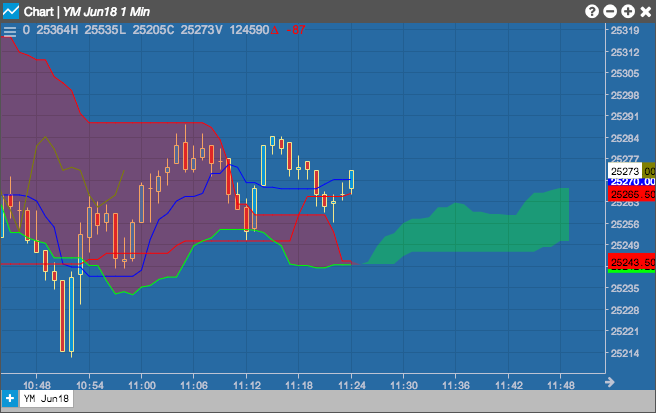
Charts
Ichimoku Clouds (ICH)
The Ichimoku Clouds study was developed by Goichi Hosoda pre-World War II as a forecasting model for financial markets. The study is a trend following indicator that identifies mid-points of historical highs and lows at different lengths of time and generates trading signals similar to that of moving averages or MACD. A key difference between Ichimoku and moving averages is Ichimoku charts lines are shifted forward in time creating wider support/resistance areas mitigating the risk of false breakouts.
The area between the two span lines forms the cloud. It is a thicker version of normal support and resistance lines that takes volatility into account. A break through the cloud and a subsequent move above or below it can indicate that the trend will continue in that direction.
Configuration Options
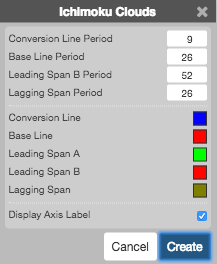
- Conversion Line Period: Number of periods to use for the conversion line calculations.
- Base Line Period: Number of periods to use for the base line calculations.
- Leading Span B Period: Number of periods to use for the leading span calculations.
- Laggins Span Period: Number of periods to use for the lagging line calculations.
- Color Selectors: Colors to use for graph elements.
- Display Axis Label: Whether to display the most recent value on the Y axis.
Formula
\[Conversion\;Line = \frac{( Highest High_{cl-periods} + Lowest Low_{cl-periods} )}{2}\;for\;the\;past\;cl-periods\]
\[Base\;Line = \frac{( Highest High_{bl-periods} + Lowest Low_{bl-periods} )}{2}\;for\;the\;past\;bl-periods\]
\[Leading\;Span\;A = \frac{( Base\;Line + Conversion\;Line )}{2} \;plotted\;n-periods\;ahead\;of\;the\;current\;bar\]
\[Leading\;Span\;B = \frac{( Highest High + Lowest Low )}{2}\; for\;the\;past\;b-periods,\;plotted \\ \;m-periods\;ahead\;of\;current\;bar\]
\[Cloud = Shaded\;Area\;between\;Span\;A\;and\;Span\;B\]
\[Lagging\;Span = EMA_{x}\;plotted\; \frac{x}{2} \;periods\;behind\]